Introduction
Managing taxes efficiently is an essential part of financial planning. Many individuals confuse tax planning with tax saving, assuming they are the same. However, understanding the difference between the two is crucial for effective financial management.
Tax planning is a strategic approach to legally minimizing tax liability, while tax saving focuses on utilizing specific provisions and deductions to reduce tax outflow in the short term. By adopting the right tax planning strategies, individuals can optimize their tax liabilities while taking advantage of tax-saving investments.
What is Tax Planning?
Tax planning involves structuring finances in a way that maximizes tax benefits while ensuring compliance with tax laws. It is a long-term approach aimed at optimizing tax liability through careful financial decisions. Tax planning is not just for a particular year but should be approached as a continuous process throughout life. It is about structuring finances in a way that benefits you in the long run while carrying your income tax file accordingly, considering all incomes, including family income. Tax planning is applicable not just for individuals but also for corporations, as businesses plan their taxes to maximize profits and ensure tax efficiency.
Key Aspects of Tax Planning:
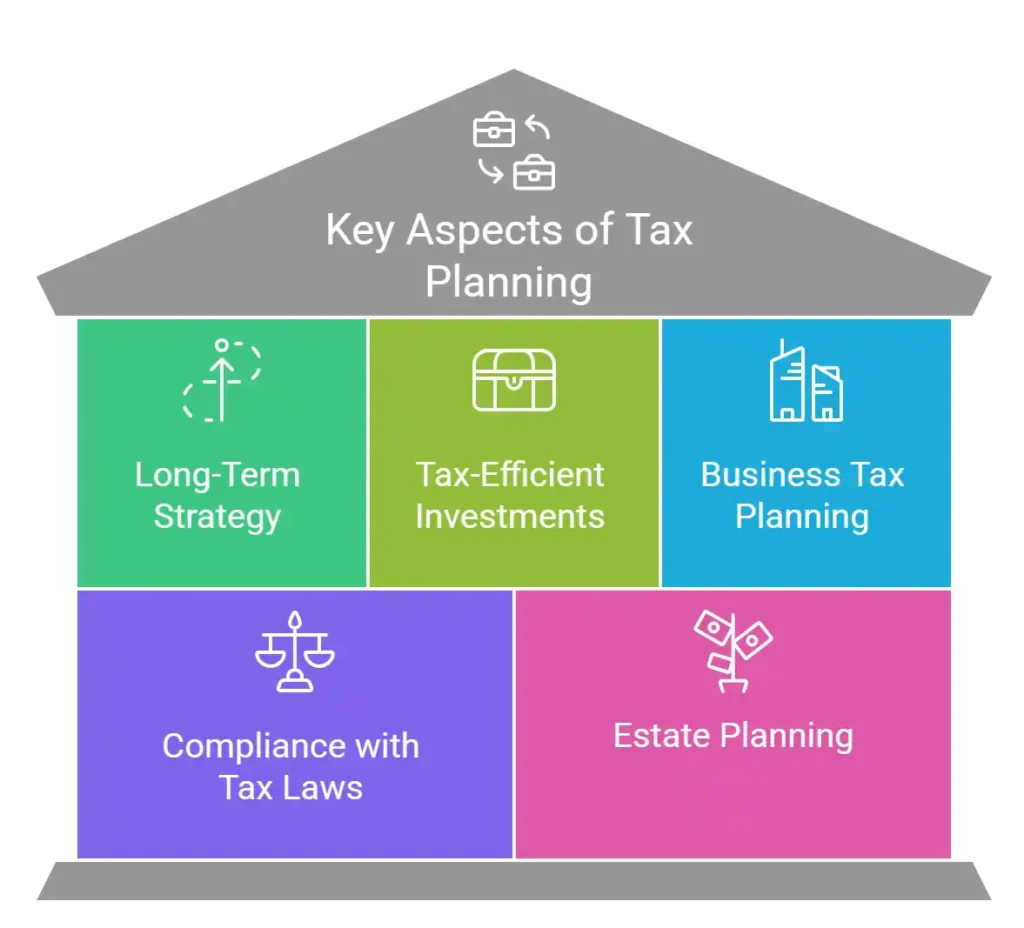
- Long-Term Strategy: Tax planning is not just about saving money in the current financial year but also about reducing tax liabilities in the long run.
- Utilization of Tax-Efficient Investments: Investing in financial instruments such as Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS), Public Provident Fund (PPF), and National Pension System (NPS) to gain tax benefits. These are crucial tax-saving investments that also help in wealth creation.
- Business Tax Planning: Companies and businesses optimize their expenses, depreciation, and investments to ensure tax efficiency.
- Compliance with Tax Laws: Ensuring that all tax planning strategies are legal and in accordance with the country’s tax regulations.
- Estate Planning: Organizing finances and assets in a way that minimizes tax liabilities upon inheritance or transfer of wealth.
What is Tax Saving?
Tax saving refers to the methods used to reduce tax liabilities by availing tax deductions, exemptions, and rebates available under the Income Tax Act. Tax saving is generally for a very short-term purpose, usually for a particular financial year. More specifically, the need for tax saving arises towards the end of the year, especially in March, when individuals seek to invest in tax-saving instruments before the financial year closes. Unlike tax planning, which is relevant for both individuals and corporations, tax saving is primarily beneficial for individuals, as most tax-saving instruments are designed for personal income tax reductions. Tax saving is part of tax planning, but tax planning is not a part of tax saving.
Key Aspects of Tax Saving:
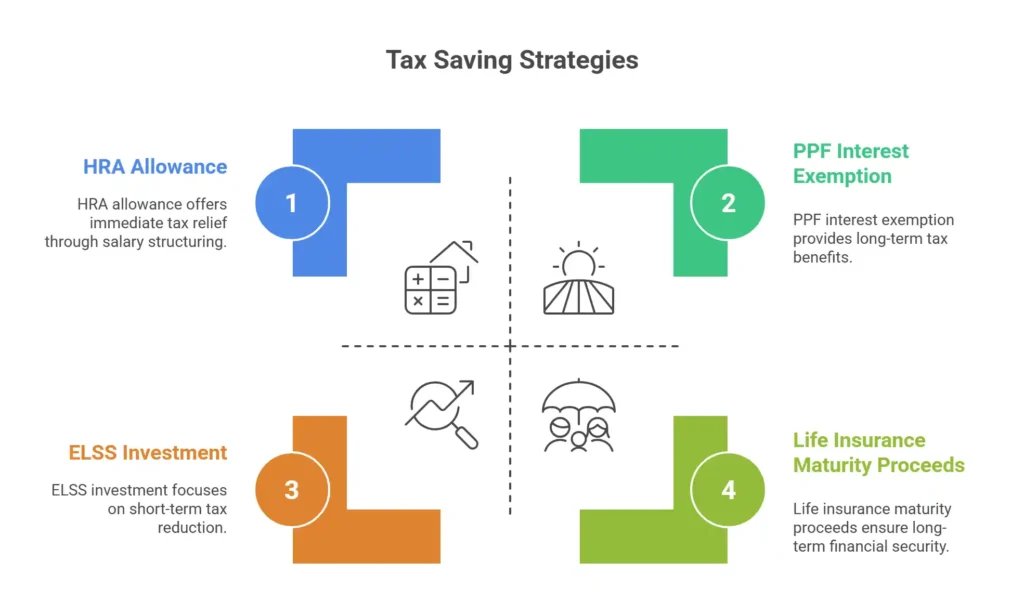
- Utilization of Tax-Saving Investments: Investments under Section 80C, such as ELSS, PPF, and Life Insurance, help in reducing taxable income.
- Short-Term Focus: The primary objective is to reduce tax payments for the current financial year.
- Making Use of Deductions: Tax deductions for medical insurance under Section 80D, home loan interest under Section 24(b), and educational loan interest under Section 80E.
- Tax Exemptions: Certain income sources, such as interest earned on the PPF or maturity proceeds of life insurance policies, are exempt from tax.
- Salary Structuring: Employees can use allowances like HRA, LTA, and meal vouchers to save taxes.
Tax Planning vs. Tax Saving

Understanding the distinction between tax planning strategies and tax saving is essential to make informed financial decisions.
| Aspect | Tax Planning | Tax Saving |
| Objective | Long-term financial efficiency | Immediate tax reduction |
| Approach | Strategic and proactive | Reactive and last-minute |
| Focus | Holistic financial planning | Specific deductions and exemptions |
| Time Horizon | Long-term benefits | Short-term relief |
| Applicability | Individuals and Corporations | Mostly Individuals |
| Examples | Investing in tax-saving investments like ELSS, PPF, and NPS | Claiming deductions under Section 80C, 80D, and 24(b) |
Income Tax Planning Tips for Maximizing Benefits
To maximize tax efficiency, one must integrate income tax planning tips with tax-saving investments. Here are some key tips:
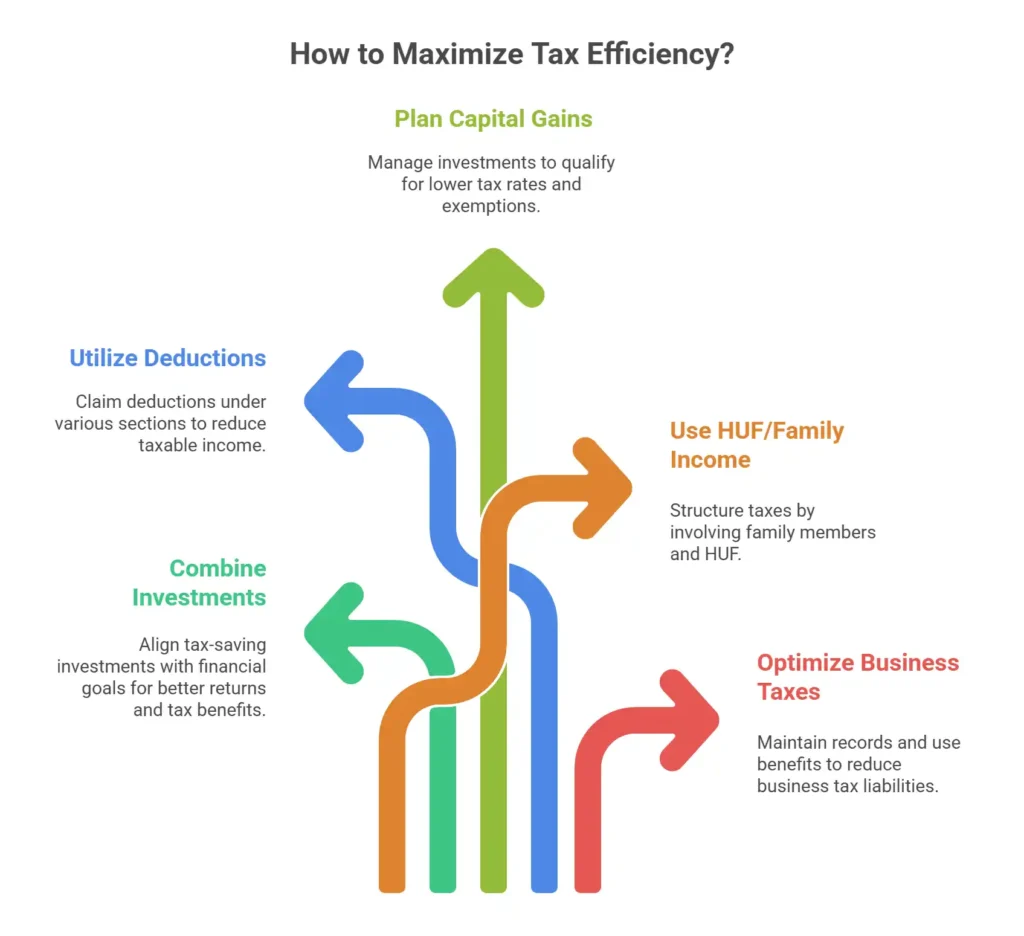
1. Combine Tax Planning with Tax-Saving Investments
Instead of focusing only on deductions, align tax-saving investments with financial goals. For instance:
- If saving for retirement, consider NPS or PPF.
- If looking for higher returns, opt for ELSS, which provides tax benefits and potential wealth creation.
- If planning for children’s education, use Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) or tax-free fixed deposits.
2. Take Advantage of Allowable Deductions
- Use Section 80C to claim deductions up to ₹1.5 lakh annually.
- Avail medical insurance benefits under Section 80D.
- Reduce tax on home loans under Sections 80C and 24(b).
- Leverage Section 80G for tax benefits on donations to charitable institutions.
3. Plan for Capital Gains Tax
If you have investments in stocks or real estate, plan your transactions wisely to reduce capital gains tax. Holding investments for a longer duration may qualify them for lower tax rates. Capital gains exemptions under Sections 54 and 54F can help reduce tax burdens.
4. Use HUF and Family Members’ Income for Tax Benefits
Forming a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) or investing in the name of a spouse or children can help in better tax structuring.
5. Optimize Business Tax Planning
For businesses, maintaining proper records, using depreciation benefits, and structuring salaries with allowances and perquisites can significantly reduce tax liabilities. Implementing the right income tax planning tips can result in maximum tax savings.
Conclusion
Both tax-planning strategies and tax-saving investments are essential for effective financial management. While tax saving helps reduce immediate tax outgo, tax planning ensures long-term financial efficiency and stability. A well-balanced approach that integrates both strategies can help achieve financial goals while staying compliant with tax laws.
Consulting a financial expert or tax advisor can further enhance your tax efficiency and provide customized income tax planning tips based on individual needs. With proper tax planning, individuals and businesses can save substantial amounts while securing financial stability for the future.









